What is Fiber Optic GPON?
Understanding the Future of Connectivity: What's the Deal with Fiber Optic GPON?
In today's world where speed is everything ,the fast reliable internet is pretty much essential for everything from streaming 4K video and intense online gaming to running all sorts of business operations and hosting cloud services. If you've been browsing around looking for a better internet setup than what you have now ,you've probably come across the term Fiber Optic GPON. But what exactly is it and why do experts consider it the gold standard for high-speed connectivity?
This in-depth guide will give you a clear idea of the tech behind GPON ,explain how it works and show you why it's the kind of connection you need to future-proof your home or business network.
The Alphabet Soup Explained: What GPON Actually Stands For
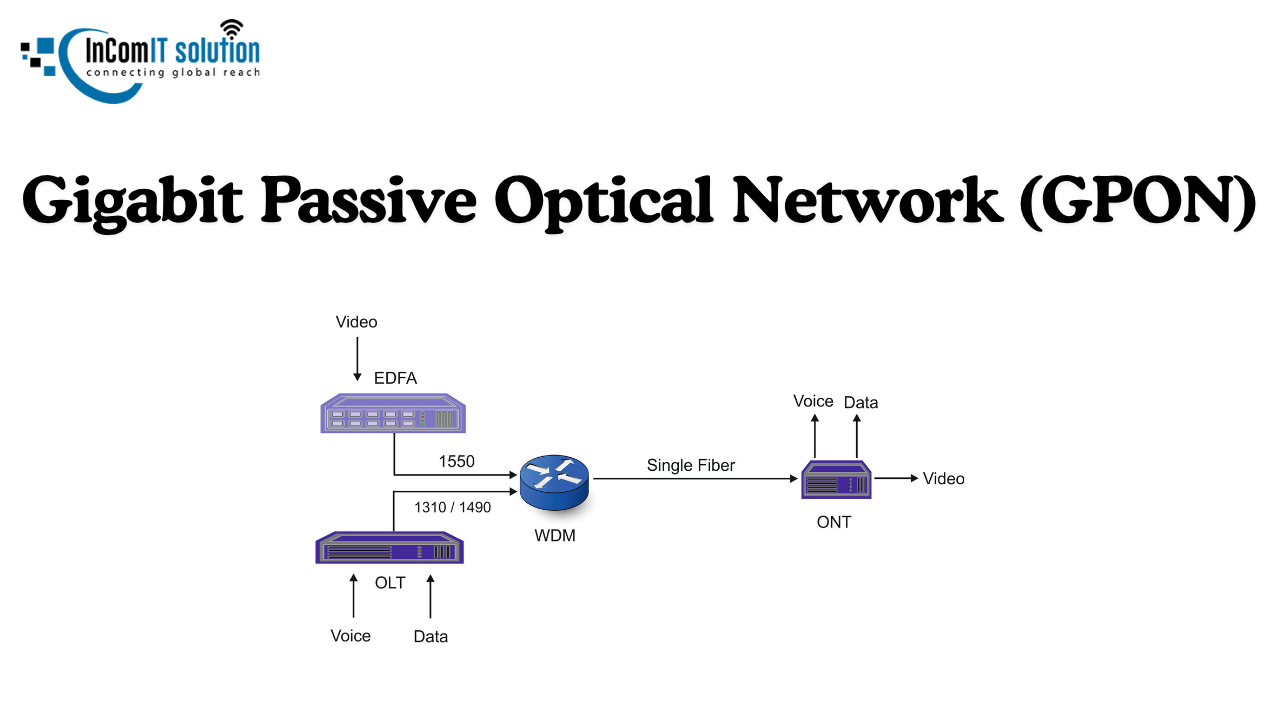
GPON is an acronym for Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network. Let's break that down :
Gigabit-capable: In simple terms this means the network is designed to handle an enormous amount of data ,with speeds often reaching up to 2.488 Gigabits per second (Gbps) or downstream and 1.244 Gbps upstream , though most internet service providers only market typical home plans at 100 Mbps ,500 Mbps or 1 Gbps.
Passive Optical: And that's where it gets really interesting. "Optical" is all about the use of fiber optic cables ,which transmit data by pulsing light instead of electrical signals like those used in traditional copper cables. And "Passive" simply means there's no need for electrical equipment in between the central office and your place (no splitter powering needed), which greatly reduces energy consumption and maintenance costs.
Network: Just a fancy word for the whole system of connections that lets data get shared around.
So in essence a Fiber Optic GPON connection is a highly efficient ,high-speed network that uses fiber optic cables and some clever passive components to deliver data right to your door.
What Makes the GPON System Tick?
The structure of a GPON network is pretty clever. It uses a point-to-multipoint setup ,meaning you can get a single strand of fiber from the provider's central office split to serve several users.
Here are the key bits and how they work together:
Optical Line Terminal (OLT):
That's the network endpoint at the Internet Service Provider's (ISP) central office.
The OLT is basically the 'brain' that pulls in data from the internet backbone and sends it as light pulses down the fiber optic line.
And it controls and manages traffic flow to and from the users.
Optical Splitter:
It's just a small ,harmless passive device typically installed inside a cabinet or junction box near your place.
It splits the light signal coming from the OLT to multiple separate fiber lines which run to individual homes or businesses. A common split ratio is 1:32 or 1:64.

Shutterstock
Optical Network Terminal Unit (ONT/ ONU):
This is that little box or device you've probably got sitting inside your home or business (often that fibre modem of yours).
The ONT picks up the light signal from the splitter and turns it back into electrical signals that your computer, router, and other devices can actually use. It also turns your outgoing electrical signals back into light pulses to send back up to the internet.
This is what lets providers offer such fast (low latency) and high-speed (high bandwidth) connections.
Why Choose GPON? The Unbeatable Advantages
When you're shopping around for a fibre internet plan it's worth doing your research and finding out a bit about the GPON technology behind it. That way you can make a more informed decision.
1. Lightening Fast and Symmetrical Speeds
Loads of Bandwidth: GPON is capable of much faster download speeds than traditional DSL or cable internet.
Symmetrical Speeds : While packages vary, fibre is inherently good for symmetrical speeds (upload speed is the same as download speed), which is a big deal for things like remote work, video conferencing, cloud backups, and creating online content.
2. Unmatched Reliability and Low Latency
Fibre Lasts: Fibre optic cables are not affected by electromagnetic interference (EMI) or radio-frequency interference (RFI), which is a common problem with copper lines. This means you get a cleaner, more stable signal, even over long distances or in bad weather.
Low Latency: Because data travels at the speed of light and there aren't all those power-hungry bits of kit in between (just a passive network), the delay (latency) is a lot less. This is a game-changer for gamers and anyone else who needs a near-instant response time.
3. Future-Proof Technology (SEO/Premium Content Advantage)
Upgrade Any Time: The fibre infrastructure already built for GPON can be easily upgraded to next-generation technologies like XGS-PON or NG-PON2, which can do speeds of 10 Gbps and faster - all you need to do is get some new bits of kit for your OLT and ONT, not dig up the whole cable. This makes fibre a long-term investment in your internet.
The GPON Connection in Your Local Area
Fibre networks powered by GPON are rolling out all over the place - from the tech hubs of places like New York City to the residential areas of cities like London.
If you are in an area with a competitive fibre market, an independent ISP using GPON might offer a better balance of speed, cost, and reliability than the bigger providers. Always check the available speeds and prices in your specific area to get the best value.
Final Verdict: Upgrade to GPON
It's time to ask yourself - "What's holding me back from switching to fibre?"
Fibre Optic GPON is the sort of tech that gives you the very fastest and most reliable internet available to consumers today. Its the foundation for the high-speed future we are all moving towards.
Ready to experience the full potential of the internet? Get in touch with your local ISPs and ask about their fibre plans.









